Introduction to coordinate systems
Overview
To define the precise location of surveyed objects in the world, you need to set up a
Coordinate system is a coordinate-based local, regional or global system used to locate geographical entities. A spatial reference system defines a specific map projection, as well as transformations between different spatial reference systems.
When choosing a
Coordinate system is a coordinate-based local, regional or global system used to locate geographical entities. A spatial reference system defines a specific map projection, as well as transformations between different spatial reference systems.
Coordinate system is a coordinate-based local, regional or global system used to locate geographical entities. A spatial reference system defines a specific map projection, as well as transformations between different spatial reference systems.
Rover is one of the two GNSS receivers that is used for collecting data in RTK or PPK scenarios. Rover is a moving unit: the surveyor uses rover to record the points, while rover receives the corrections from the static base.
You cannot change the CS settings once the project is created.
A mismatch in the CS setup between your
Rover is one of the two GNSS receivers that is used for collecting data in RTK or PPK scenarios. Rover is a moving unit: the surveyor uses rover to record the points, while rover receives the corrections from the static base.
Base is one of the receivers that act as a reference station in RTK or PPK scenarios. It is a static unit with the determined coordinates that sends corrections to the moving unit or rover. If the base is set over the known point, it provides absolute accuracy.
Setup
You can set up the CS for your project in several ways.
Choose from the library
Emlid Flow and Emlid Flow 360 contain the verified registry of local CSs for specific countries. Every
Coordinate system is a coordinate-based local, regional or global system used to locate geographical entities. A spatial reference system defines a specific map projection, as well as transformations between different spatial reference systems.
Rover is one of the two GNSS receivers that is used for collecting data in RTK or PPK scenarios. Rover is a moving unit: the surveyor uses rover to record the points, while rover receives the corrections from the static base.
The Networked Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol or NTRIP network is an alternative source of corrections. NTRIP allows your rover to accept corrections over the Internet with no need for the second local receiver acting as a base. A reference station collects data, then sends it to NTRIP caster, where it is retransmitted through the Internet port to the client rover connected via a particular port and authorized.
In this case, the apps apply
Grid distance is the distance measured on the projection flat plane.
Grid North azimuth is the angle measured clockwise between a line parallel to the central meridian, and the direction to a point of interest (a straight line between two points on the projection flat plane).
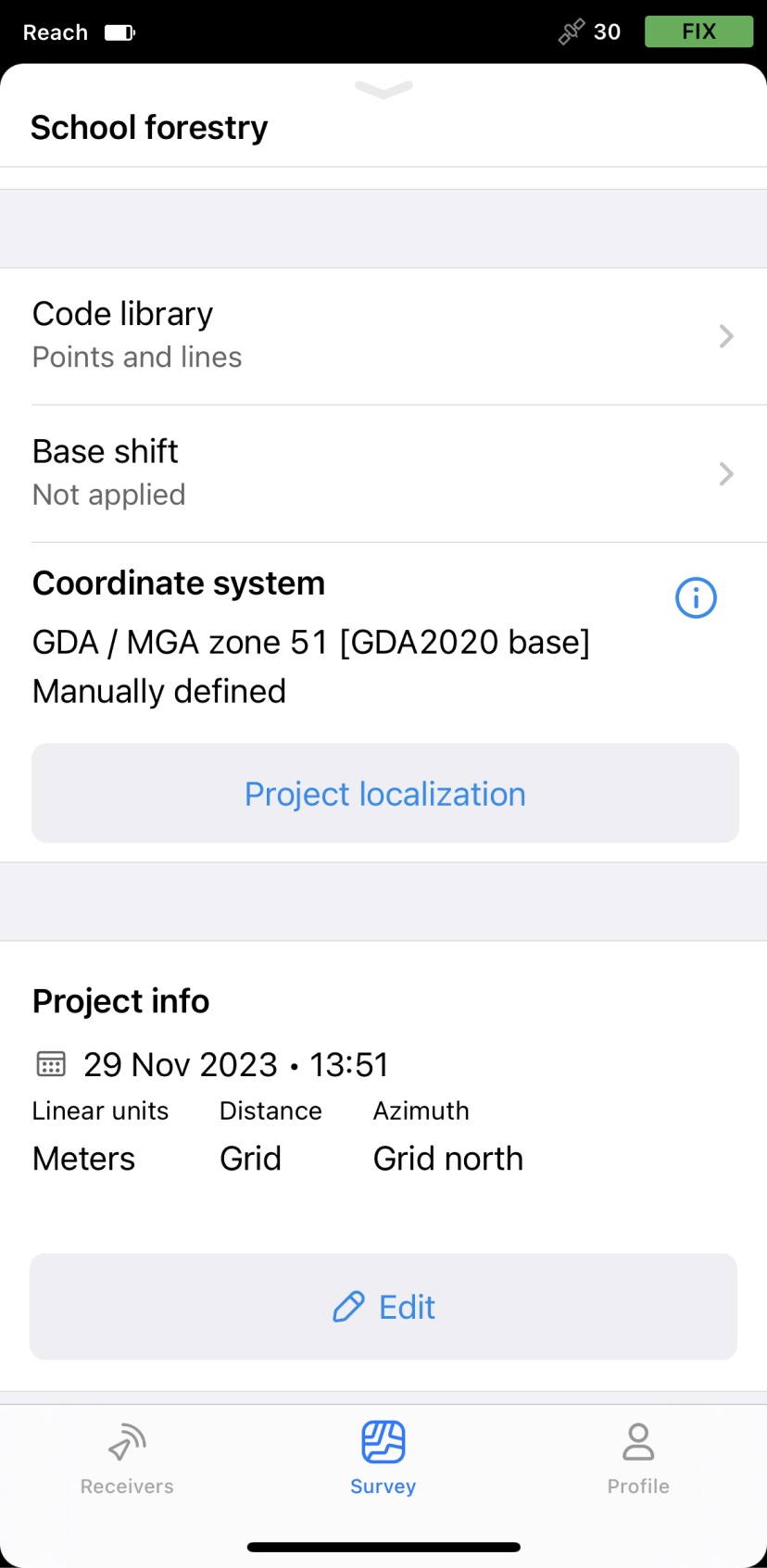
Below is an example of a local
Coordinate system is a coordinate-based local, regional or global system used to locate geographical entities. A spatial reference system defines a specific map projection, as well as transformations between different spatial reference systems.
Rover is one of the two GNSS receivers that is used for collecting data in RTK or PPK scenarios. Rover is a moving unit: the surveyor uses rover to record the points, while rover receives the corrections from the static base.
The Networked Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol or NTRIP network is an alternative source of corrections. NTRIP allows your rover to accept corrections over the Internet with no need for the second local receiver acting as a base. A reference station collects data, then sends it to NTRIP caster, where it is retransmitted through the Internet port to the client rover connected via a particular port and authorized.
California zone 5—a projection.
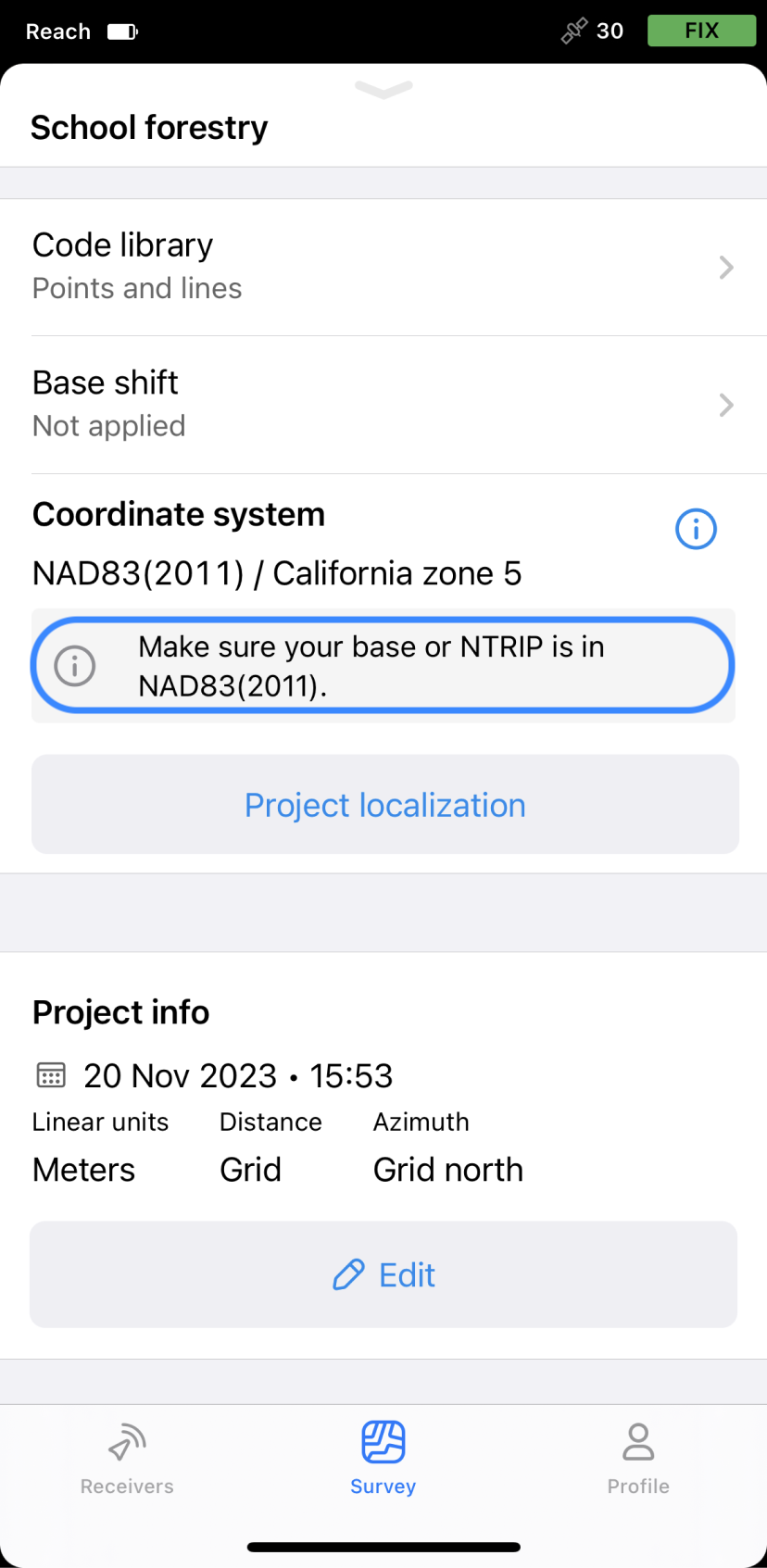
Apply global CS
This option is used to get started with the Emlid Flow app and quick tests in the field. As a result, you get geographic coordinates—latitude, longitude, ellipsoid height—in the datum of your base.
In this case, the apps apply
Ground distance is the distance measured on the actual surface of the Earth, taking the mean elevation of the measured points into account.
True North azimuth is the angle ranging from 0 to 360 degrees measured clockwise between True North and the direction to a point of interest.
Below is an example of using the Global CS option in Emlid Flow & Emlid Flow 360. If you enter the base coordinates in NAD83(2011) in the Base settings, you’ll get the NAD83(2011) coordinates with the
Rover is one of the two GNSS receivers that is used for collecting data in RTK or PPK scenarios. Rover is a moving unit: the surveyor uses rover to record the points, while rover receives the corrections from the static base.
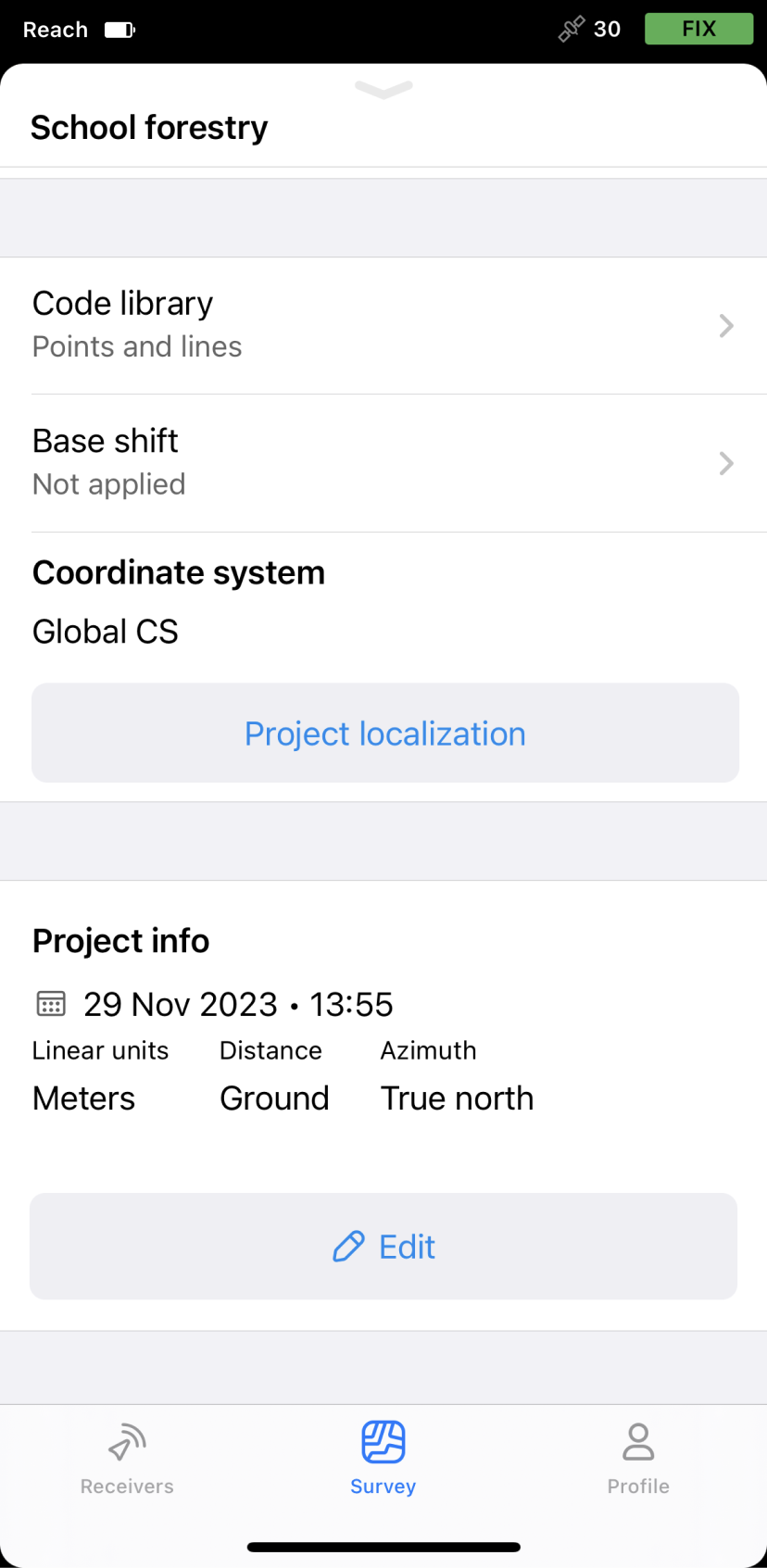
Use custom CS
If you know the projection parameters and the required local coordinate system is not supported in Emlid Flow and Emlid Flow 360, you can add your own CS by entering the following parameters:
Since not every group of parameters is required for a
Coordinate system is a coordinate-based local, regional or global system used to locate geographical entities. A spatial reference system defines a specific map projection, as well as transformations between different spatial reference systems.
- Ellipsoid your datum is based on
- Projection type and its parameters
- Transformation type and its parameters
- Geoid model
In this case, the apps apply
Grid distance is the distance measured on the projection flat plane.
Grid North azimuth is the angle measured clockwise between a line parallel to the central meridian, and the direction to a point of interest (a straight line between two points on the projection flat plane).
Below is the example of a custom CS set up in Emlid Flow.