Calculate inverse
Unlock the full set of features for topo, set-out, and as-built surveys
This guide explains how to use the Inverse tool in Emlid Flow and Emlid Flow 360 to calculate coordinate geometry data such as
Area of an object is the total amount of space enclosed by its shape on flat surface.
Direction (azimuth) of a line AB, or from point A to B, is a horizontal angle in degrees, measured at point A clockwise between the direction to the north and the direction to point B.
Overview
The Inverse tool in Emlid Flow and Emlid Flow 360 allows you to calculate geometry data for existing points. The tool can assist you in such projects as planning civil or utility engineering works and monitoring construction progress.
The software calculates the following values based on the number of input points:
When you select two and more points:
- Direction(
Direction (azimuth) of a line AB, or from point A to B, is a horizontal angle in degrees, measured at point A clockwise between the direction to the north and the direction to point B.
True North azimuth,True North azimuth is the angle ranging from 0 to 360 degrees measured clockwise between True North and the direction to a point of interest.
Grid North azimuth)Grid North azimuth is the angle measured clockwise between a line parallel to the central meridian, and the direction to a point of interest (a straight line between two points on the projection flat plane).
- Slope distance(
Slope distance from point A to point B is the length of the straight line AB, measured along the slope, taking the height difference between the points into account.
Slope Ground distance,Ground distance is the distance measured on the actual surface of the Earth, taking the mean elevation of the measured points into account.
Slope Grid distance)Grid distance is the distance measured on the projection flat plane.
- 2D distance (2D Ground distance,
2D Ground distance between points A and B is the length of the shortest AB line on the surface of the ellipsoid.
2D Grid distance)2D Grid distance between points A and B is the length of the straight line AB on a flat plane.
- Height difference
-
Grade
Grade of a line is the measure of its steepness, with larger values standing for steeper slopes and 0% indicating a horizontal line.
- Delta East(for points in a local CS only)
Delta E/N between points A and B is the difference in their coordinates along the corresponding Easting and Northing axes.
- Delta North(for points in a local CS only)
Delta E/N between points A and B is the difference in their coordinates along the corresponding Easting and Northing axes.
When you select three and more points:
- Slope distance(
Slope distance from point A to point B is the length of the straight line AB, measured along the slope, taking the height difference between the points into account.
Slope Ground distance,Ground distance is the distance measured on the actual surface of the Earth, taking the mean elevation of the measured points into account.
Slope Grid distance)Grid distance is the distance measured on the projection flat plane.
- 2D distance (2D Ground distance,
2D Ground distance between points A and B is the length of the shortest AB line on the surface of the ellipsoid.
2D Grid distance)2D Grid distance between points A and B is the length of the straight line AB on a flat plane.
-
Area
Area of an object is the total amount of space enclosed by its shape on flat surface.
-
Slope perimeter
Slope perimeter of an enclosed object is the sum of slope distances of its sides with the height difference consideration.
-
2D perimeter
2D perimeter of an enclosed object is the sum of 2D distances of its sides without the height difference consideration.
Depending on the
Coordinate system is a coordinate-based local, regional or global system used to locate geographical entities. A spatial reference system defines a specific map projection, as well as transformations between different spatial reference systems.
| CS type | Distance type | Azimuth type |
|---|---|---|
| Global CS | Ground distance Ground distance is the distance measured on the actual surface of the Earth, taking the mean elevation of the measured points into account. | True North azimuth True North azimuth is the angle ranging from 0 to 360 degrees measured clockwise between True North and the direction to a point of interest. |
| Local CS | Grid distance Grid distance is the distance measured on the projection flat plane. | Grid North azimuth Grid North azimuth is the angle measured clockwise between a line parallel to the central meridian, and the direction to a point of interest (a straight line between two points on the projection flat plane). |
See our Introduction to coordinate systems guide to learn more about distance and azimuth types in different CSs.
When calculating
Area of an object is the total amount of space enclosed by its shape on flat surface.
Coordinate system is a coordinate-based local, regional or global system used to locate geographical entities. A spatial reference system defines a specific map projection, as well as transformations between different spatial reference systems.
Area of an object is the total amount of space enclosed by its shape on flat surface.

Area of an object is the total amount of space enclosed by its shape on flat surface.
Coordinate system is a coordinate-based local, regional or global system used to locate geographical entities. A spatial reference system defines a specific map projection, as well as transformations between different spatial reference systems.
Workflow
- Emlid Flow
- Emlid Flow 360
To apply the Inverse tool in the Emlid Flow app, follow these steps:
-
Open the project in Emlid Flow.
-
Tap the tools button at the bottom left corner of the screen.
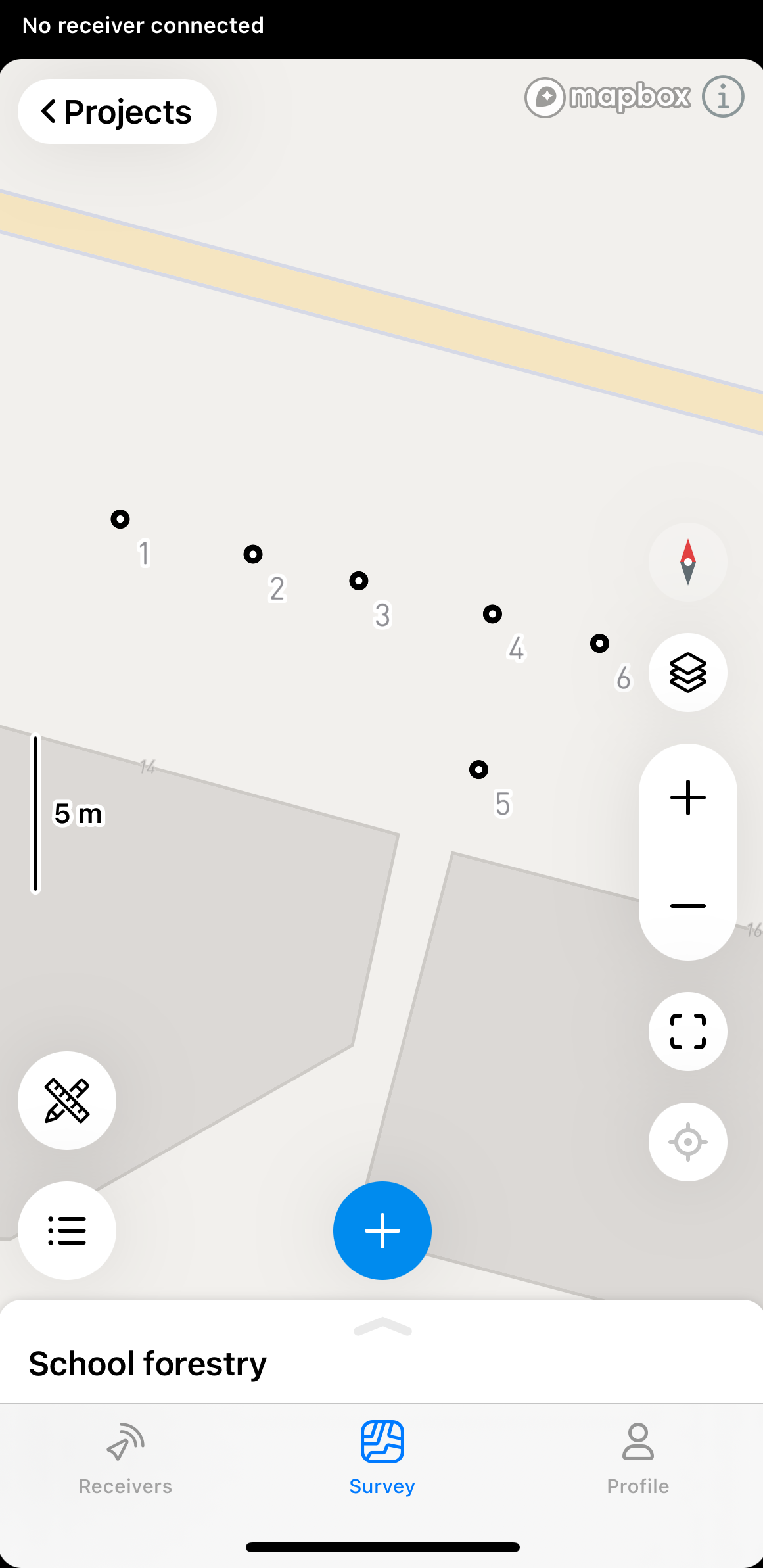
-
Tap Inverse.
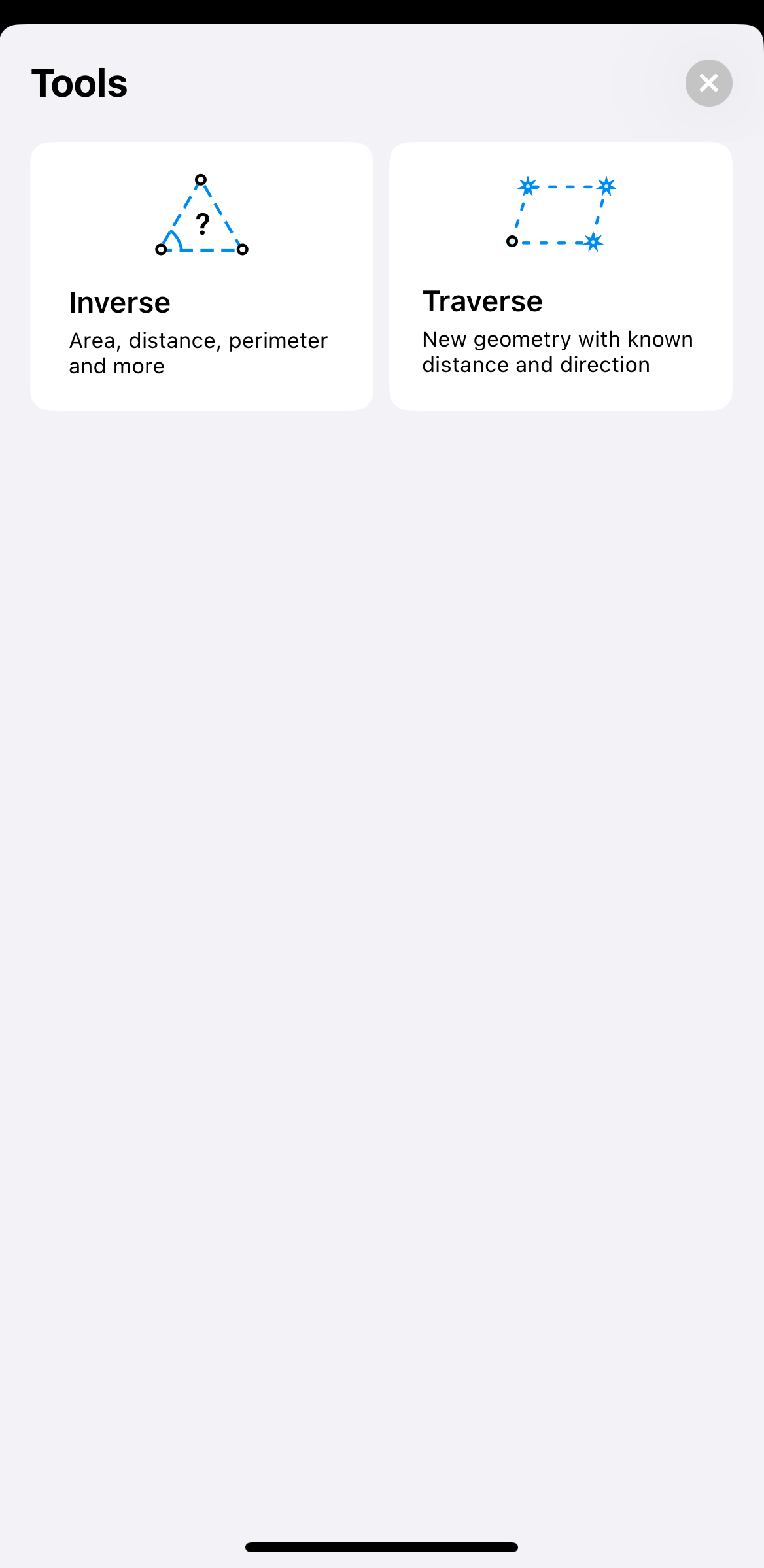
-
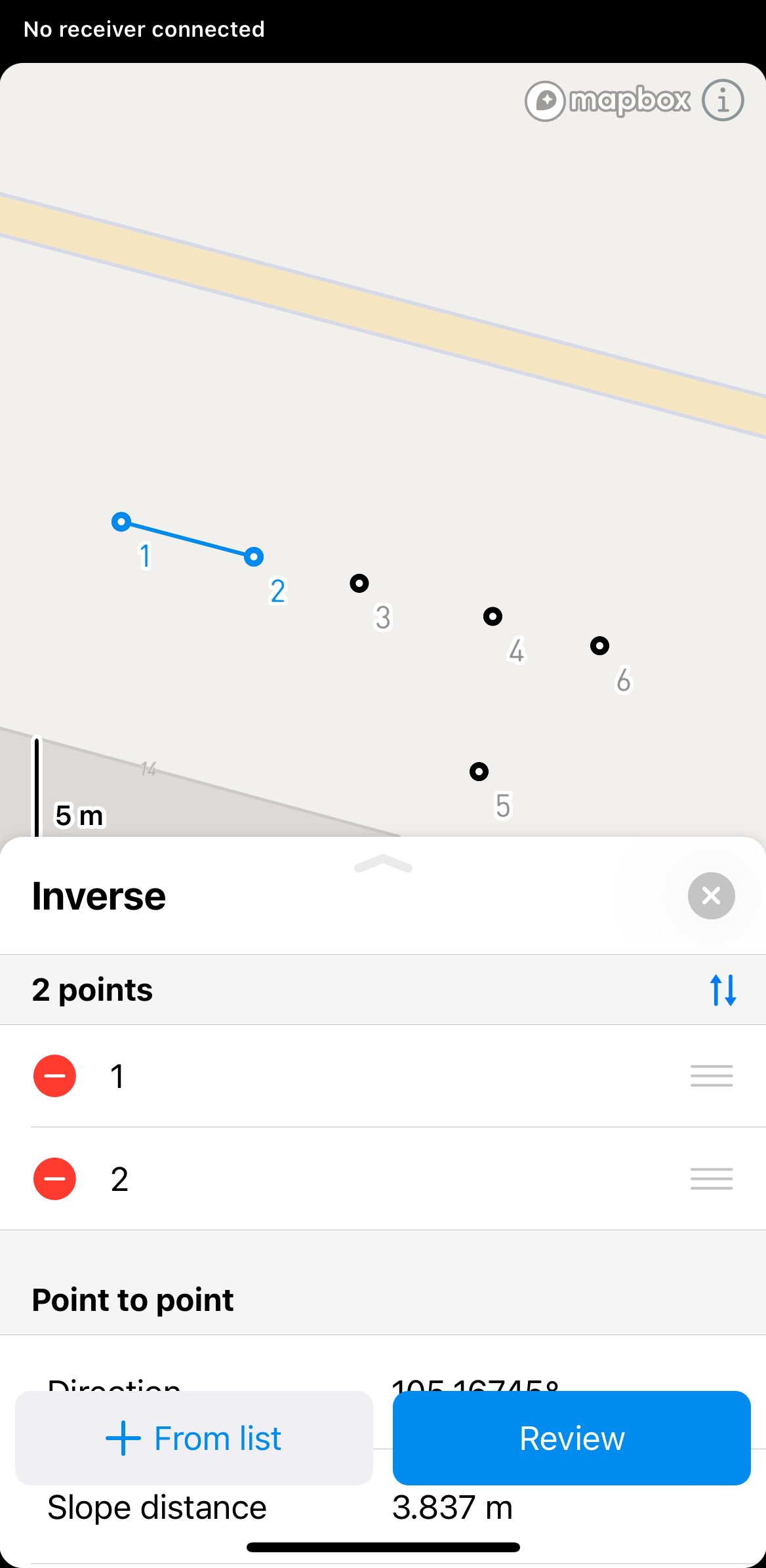
Select the points you want to calculate the inverse for from the map or Objects list.
 tip
tipIn Emlid Flow & Emlid Flow 360 you can also find the point-to-point, line, and closed line information for each line. To see this information, just tap on the line.
-
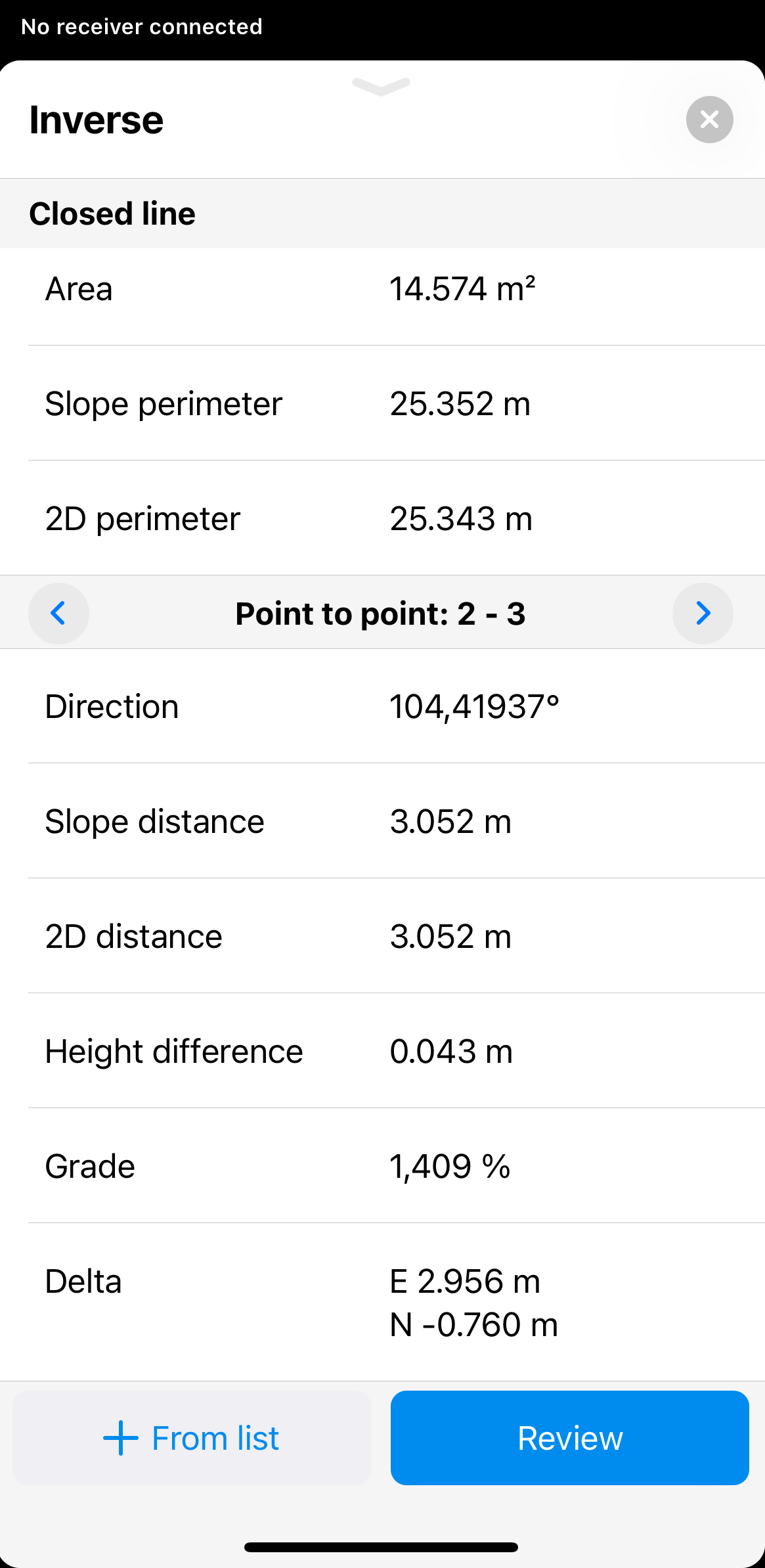
Click Review to see the calculated results. To calculate results for more than two points, use the arrow buttons to switch to a different set of two points.
noteThe displayed results will be different depending on the selected points. If you select 2 points, you'll see the point-to-point calculations. If you select 3 points, you'll also see the calculations on the area, slope perimeter, etc.
 note
noteYou can only use Closed line and Line for geometry measurements. It is not possible to import or export them as geometrical figures.
tipYou can change the order of the points in the Inverse section by dragging and dropping them. To delete a point, tap the delete button.
-
To exit the Inverse calculation mode, tap the close button in the upper-right corner.
To apply the Inverse tool in the Emlid Flow 360 app, follow these steps:
-
Open the project in Emlid Flow 360.
-
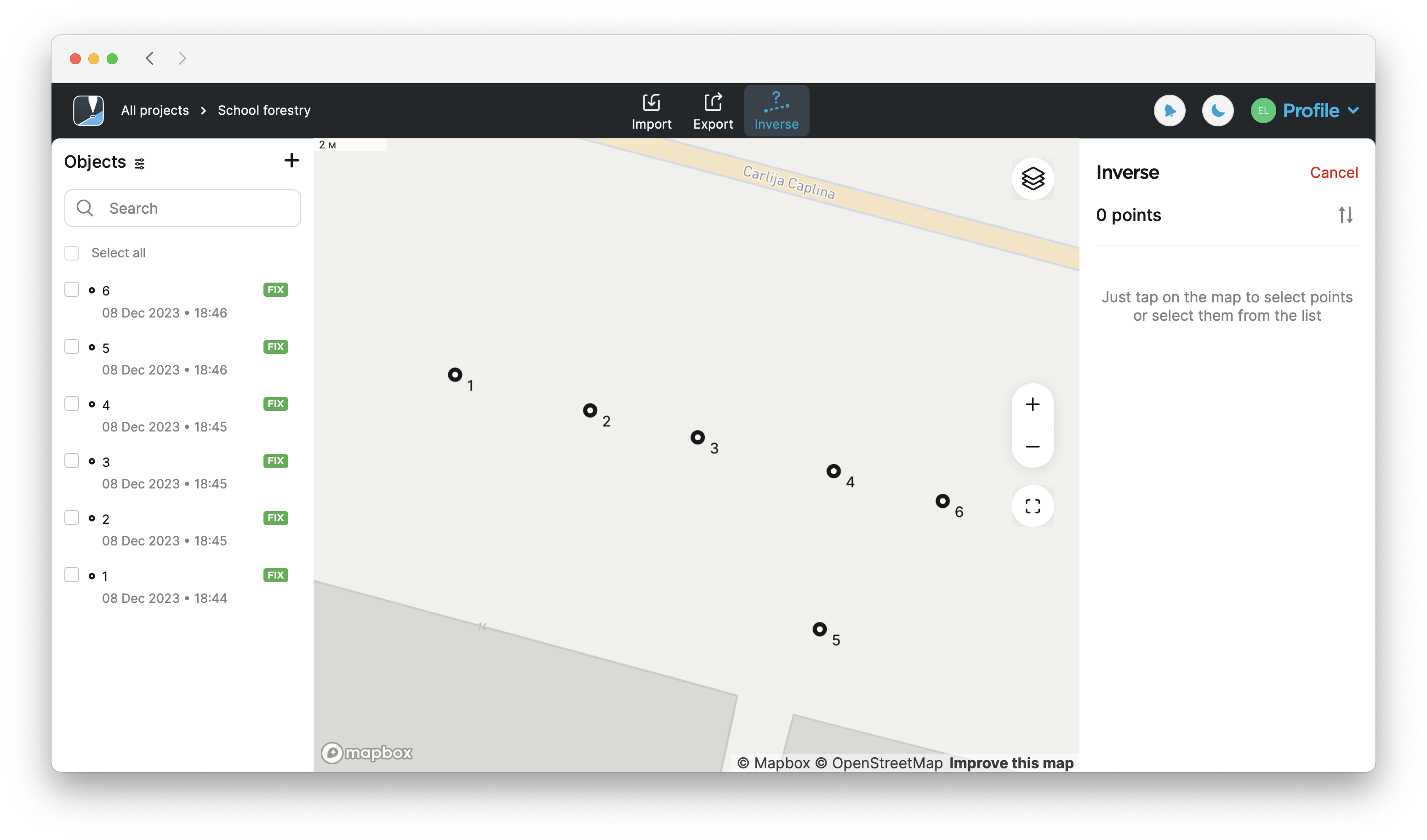
Tap Inverse at the top of the screen to calculate the results.
-
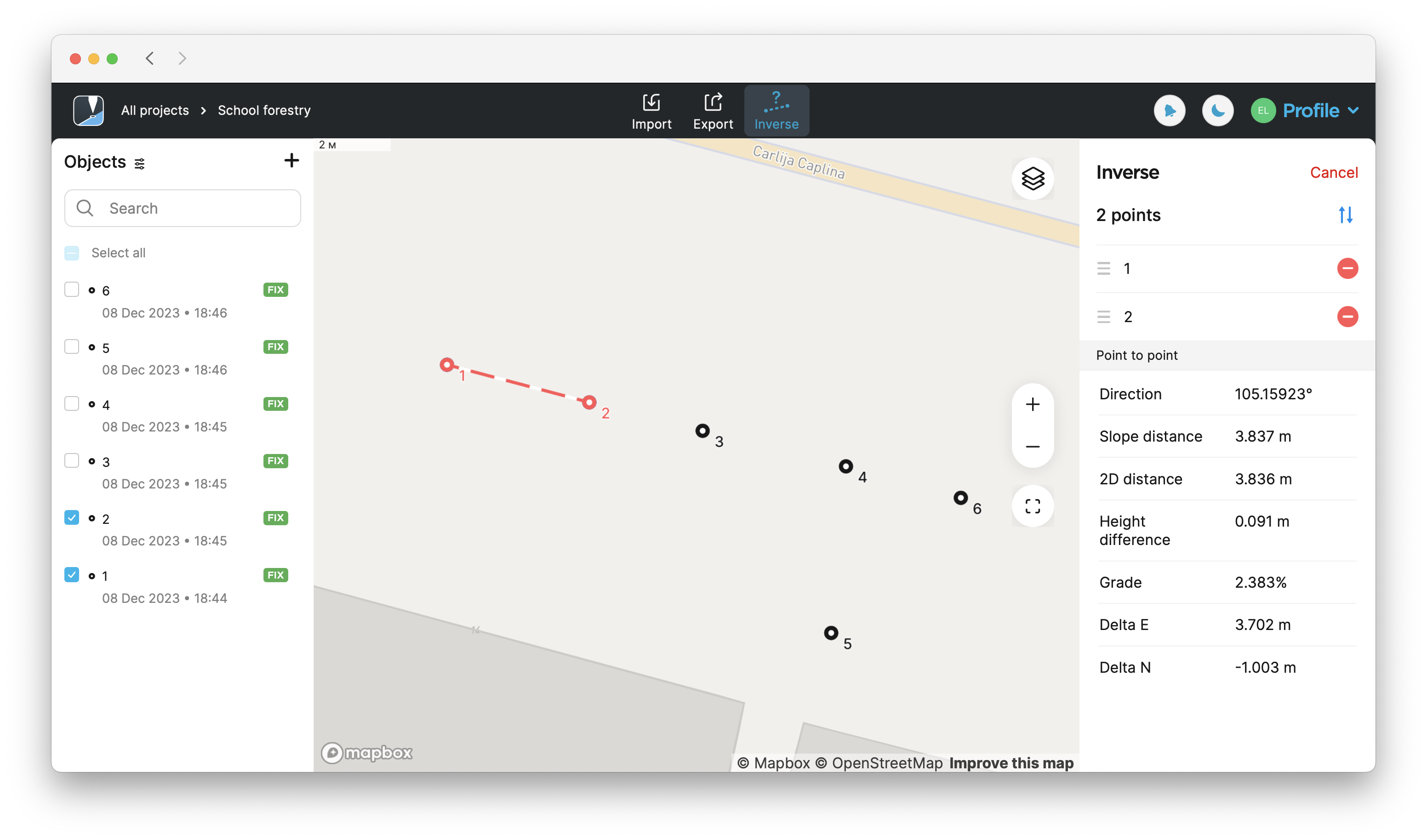
Select the points you want to calculate the inverse for from the map or Objects list.
 tip
tipIn Emlid Flow & Emlid Flow 360 you can also find the point-to-point, line, and closed line information for each line. To see this information, just tap on the line.
-
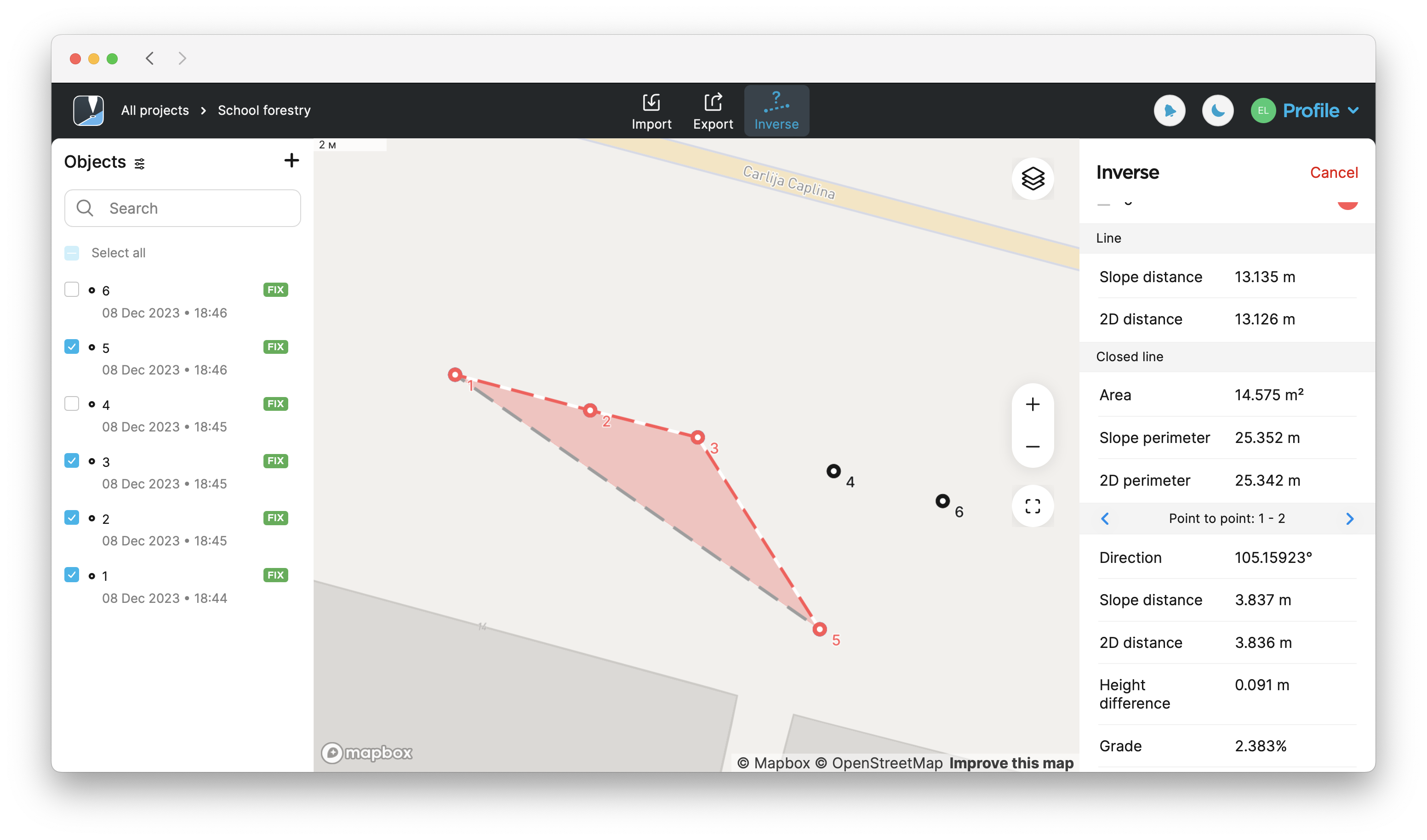
Find the calculated results on the right side of the screen. To calculate results for more than two points, use the arrow buttons to switch to a different set of two points.
noteThe displayed results will be different depending on the selected points. If you select 2 points, you'll see the point-to-point calculations. If you select 3 points, you'll also see the calculations on the
area,Area of an object is the total amount of space enclosed by its shape on flat surface.
slope perimeter, etc.Slope perimeter of an enclosed object is the sum of slope distances of its sides with the height difference consideration.
noteYou can only use Closed line and Line for geometry measurements. It is not possible to import or export them as geometrical figures.
 tip
tipYou can change the order of the points in the Inverse section by dragging and dropping them. To delete a point, tap the delete button.
-
To exit the Inverse calculation mode, tap Cancel in the upper-right corner.
Video guide
Check out the workflow in the video below: